
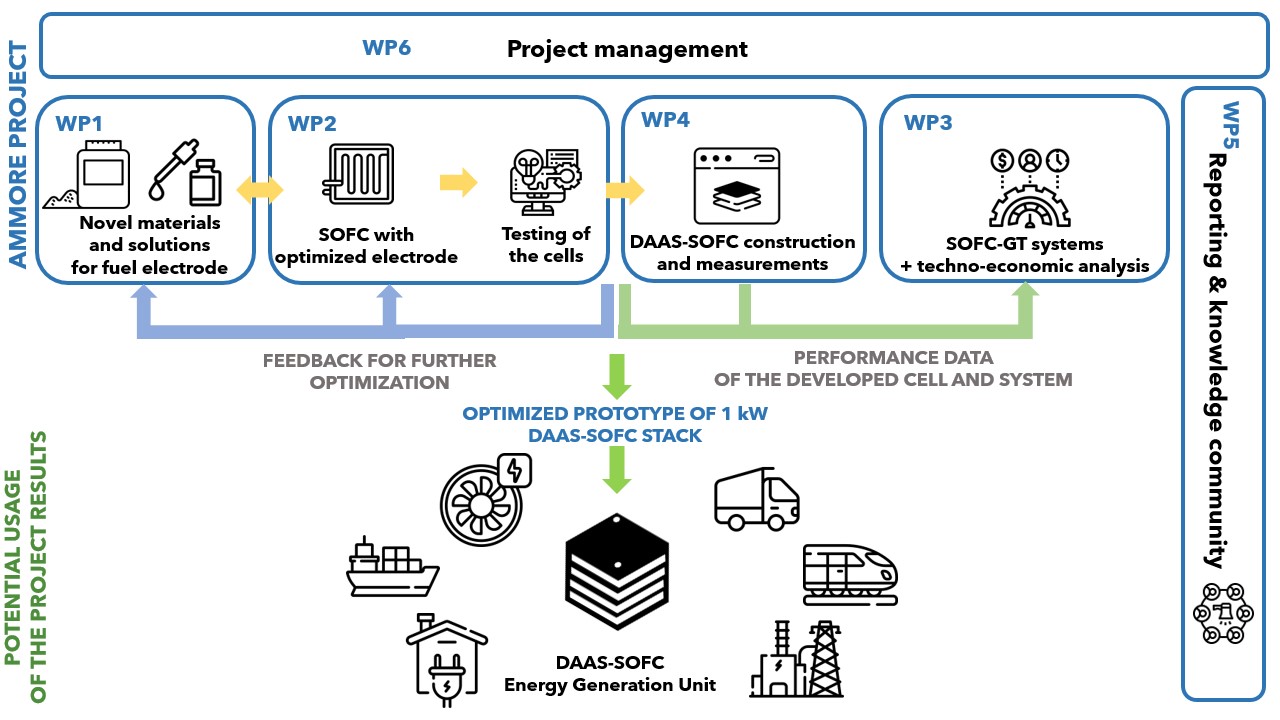
The AMMORE project aims to develop a modular, high-efficiency energy generation unit (EGU) powered directly by ammonia using solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) technology. By eliminating the need for external ammonia cracking and optimizing materials for durability and performance, AMMORE seeks to demonstrate a 1 kW-class prototype capable of clean, efficient electricity and heat generation. The project integrates advanced materials research, system modeling, and techno-economic analysis to validate ammonia as a viable, low-emission fuel alternative for transportation, hybrid SOFC–gas turbine systems, and distributed energy applications. Through collaboration among leading European research and industrial partners, AMMORE contributes to the transition toward a climate-neutral, hydrogen-based economy.
Funding and Financial Management
The AMMORE project is financially supported under the Clean Energy Transition Partnership (CETPartnership) Joint Call 2024, within the module Hydrogen & Renewable Fuels (CM2024-05). Each consortium partner receives national funding from its respective country, coordinated under the CETPartnership framework. The Institute of Power Engineering – National Research Institute (IPE-NRI, Poland) serves as the Project Coordinator and is responsible for overall financial management, ensuring proper allocation and reporting of funds according to CETPartnership and national regulations. Project partners — including institutions from Poland, Portugal, and Austria — are funded through their national innovation agencies, supporting their respective research activities in materials development, system design, modeling, and testing. IPE-NRI oversees financial reporting, payment processing, and audit coordination, ensuring transparency and efficient use of resources across the 36-month project.
Project Consortium 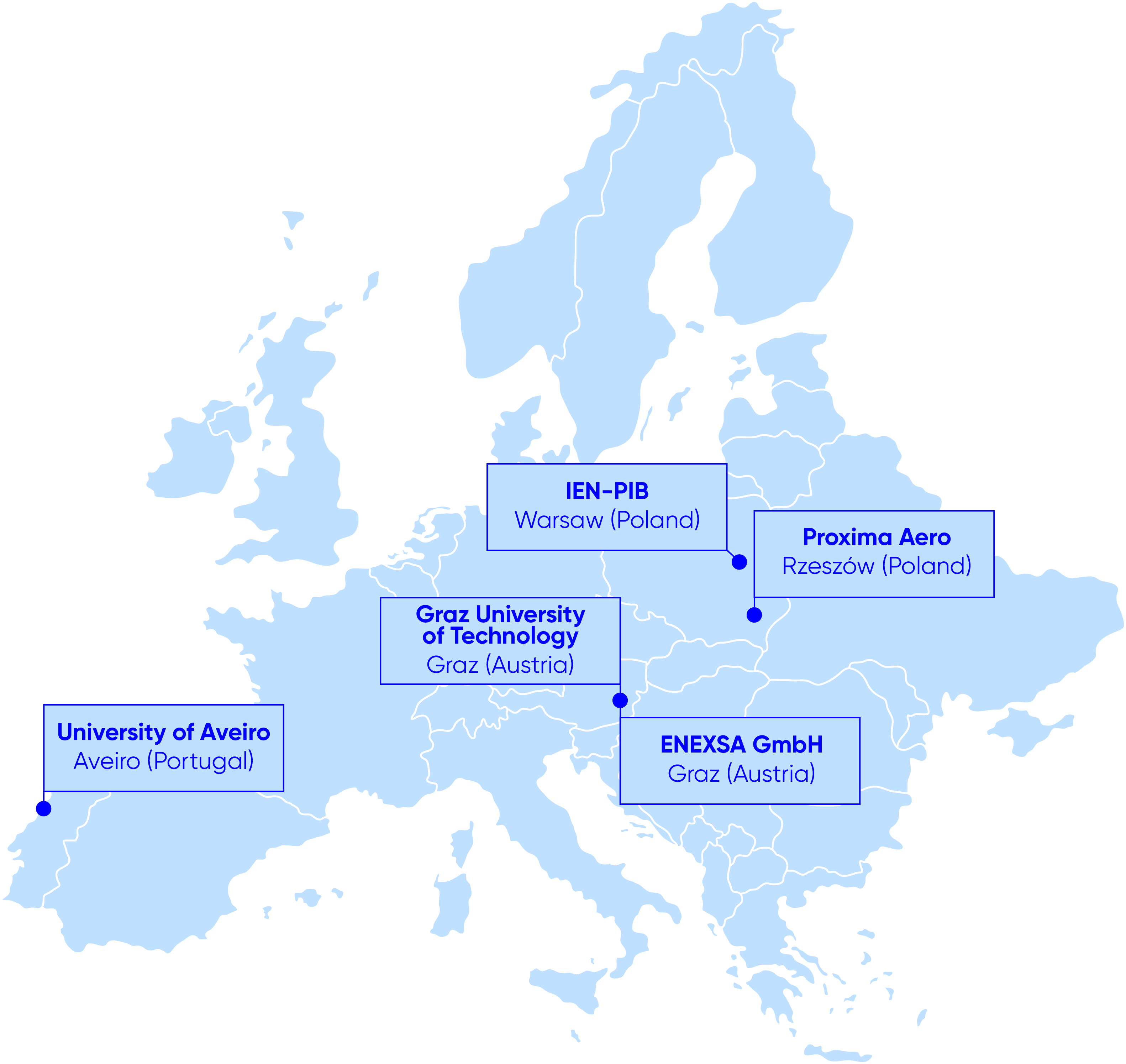
The AMMORE project brings together the key European players in SOC technology and efficient transportation solutions, representing fields of basic research as well as industrial applications. The consortium includes a national R&D center (SOC stack and system developer), two universities, andindustrial partners specializing in the power sector, hydrogen, and aviation technologies. Partners bring long-lasting expertise in H2-related fields such as materials engineering, stack integration, testing, modeling, manufacturing, and characterization (electrochemical and microstructure). Partners in the AMMORE project demonstrate an excellent track record in bringing low-TRL concepts to industrial applications at the national and international levels. With extensive experience in national and EU- projects, the consortium is well-equipped to leverage past achievements and build substantial new knowledge on top of that. Partners’ proven collaboration in bilateral and multilateral projects strengthens AMMORE’s potential to succeed. The consortium involves universities, industry representatives, and a national institute that spans the entire process from new concepts through development to technology implementation – solution meeting expectation and needs of the end-users, guiding at the same time policymakers and defining standards in the field.
- Partner 1 - Institute of Power Engineering - National Research Institute (IPE-NRI)
- Partner 2 - Proximo Aero (PxA)
- Partner 3 - University of Aveiro (UAV)
- Partner 4 - Graz University of Technology (TU Graz)
- Partner 5 - ENEXSA GmbH (ENEXSA)
The AMMORE consortium structure was strategically designed to maximize the project's success by leveraging the fully complementary expertise of each member in the SOFC field. The specialized competencies of each partner are highly synergistic, resulting in a powerful collaborative advantage. It should be highlighted that the consortium is committed to maintaining a balanced gender composition across all research, development, and scientific-technological areas, recognizing that a diverse and inclusive work environment is essential for the project's success.
The AMMORE project in numbers
 |
 |
years |
project concorcium members |
Read more about the project


